Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize the way we store and exchange data, but concerns over its energy consumption and environmental impact have been a major point of contention.
The Quadrans blockchain is a public, decentralized, and sustainable blockchain that aims to provide efficient storage and data sharing. With a focus on global scalability and process optimization, the network is designed to facilitate data management for various industries.

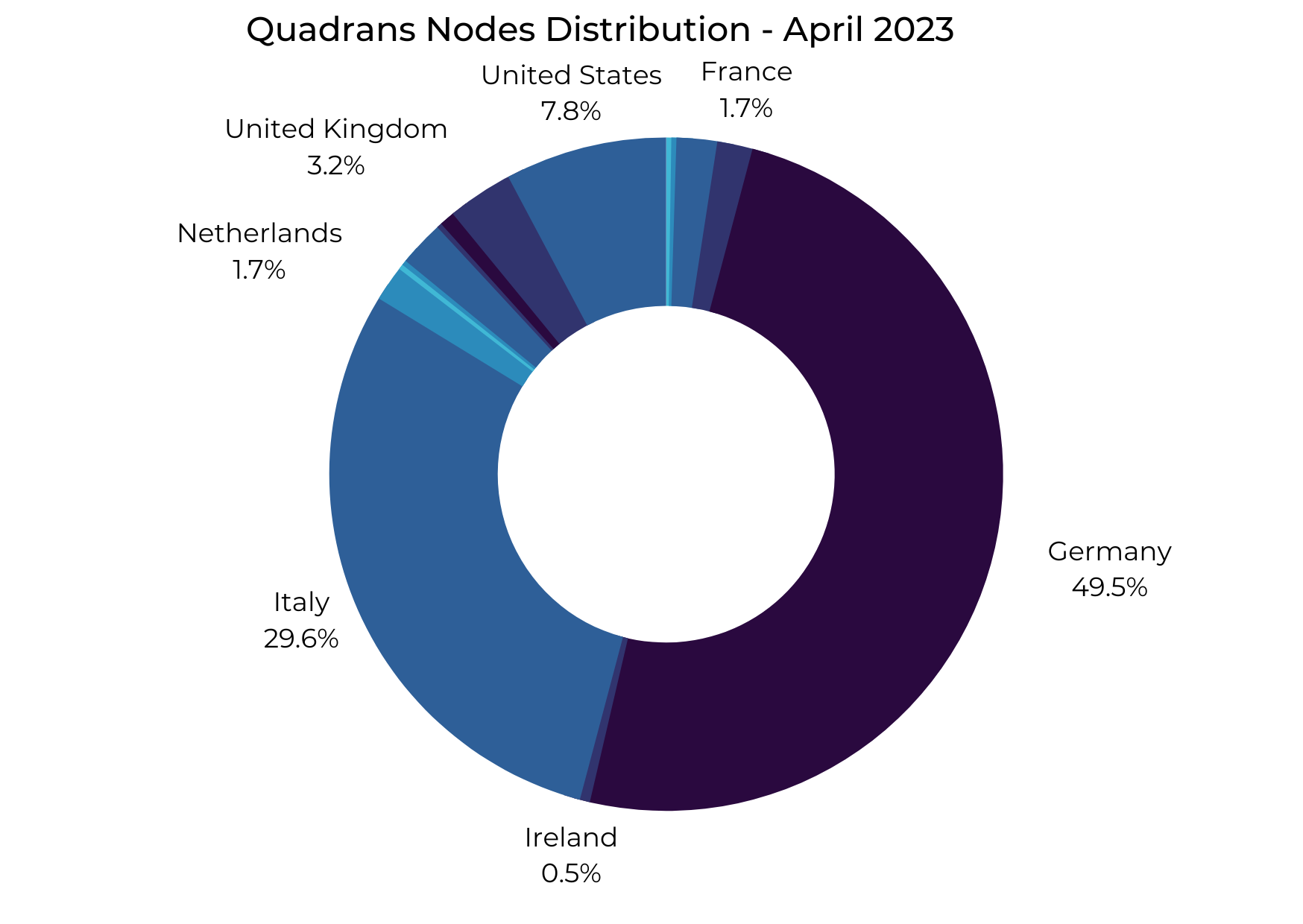
In the past year, the Quadrans Foundation conducted an extensive analysis to determine the extent of Quadrans' energy footprint. By utilizing the Network Status data available, the Foundation can instantly extract the carbon footprint of the Quadrans blockchain, considering the activity and location of nodes.
As outlined in the Yellow Paper published by the Quadrans Foundation, the energy consumption of the Quadrans Blockchain network is dependent on the number of participating nodes. As part of its commitment to sustainable growth, Quadrans is actively researching and implementing efficient consensus mechanisms that minimize energy consumption while maintaining network security and reliability. This ongoing effort is aimed at balancing the network's expansion with a reduced carbon footprint.
In addition, Quadrans places a strong emphasis on reducing the energy consumption of the hardware used in the network and promoting geographical distribution of nodes to further reduce energy usage. The blockchain algorithm is also designed to consume minimal energy when generating blocks, and it's worth noting that there's no direct correlation between energy consumption and the amount of transaction processed.
The Quadrans algorithm is designed to avoid any competition between miners, and it requires minimal computational capacity that is not dependent on the network's growth. As a result, the energy consumption of the network will not increase proportionally to the number of nodes as the network expands, ensuring that it remains energy-efficient.
The report unveils a comprehensive analysis of Quadrans' energy usage in comparison to day-to-day activities and other existing blockchain networks. It underscores how the energy cost of Quadrans' network transactions is almost insignificant in comparison to its social objective of safeguarding and storing data.
Notably, Quadrans has achieved a significantly lower carbon footprint impact compared to the first two capitalized projects.
In its commitment to sustainable growth, Quadrans continues to prioritize the minimization of energy consumption. Through ongoing research and implementation of energy-efficient technologies, we aim to maintain Quadrans network's sustainability and environmental friendliness.
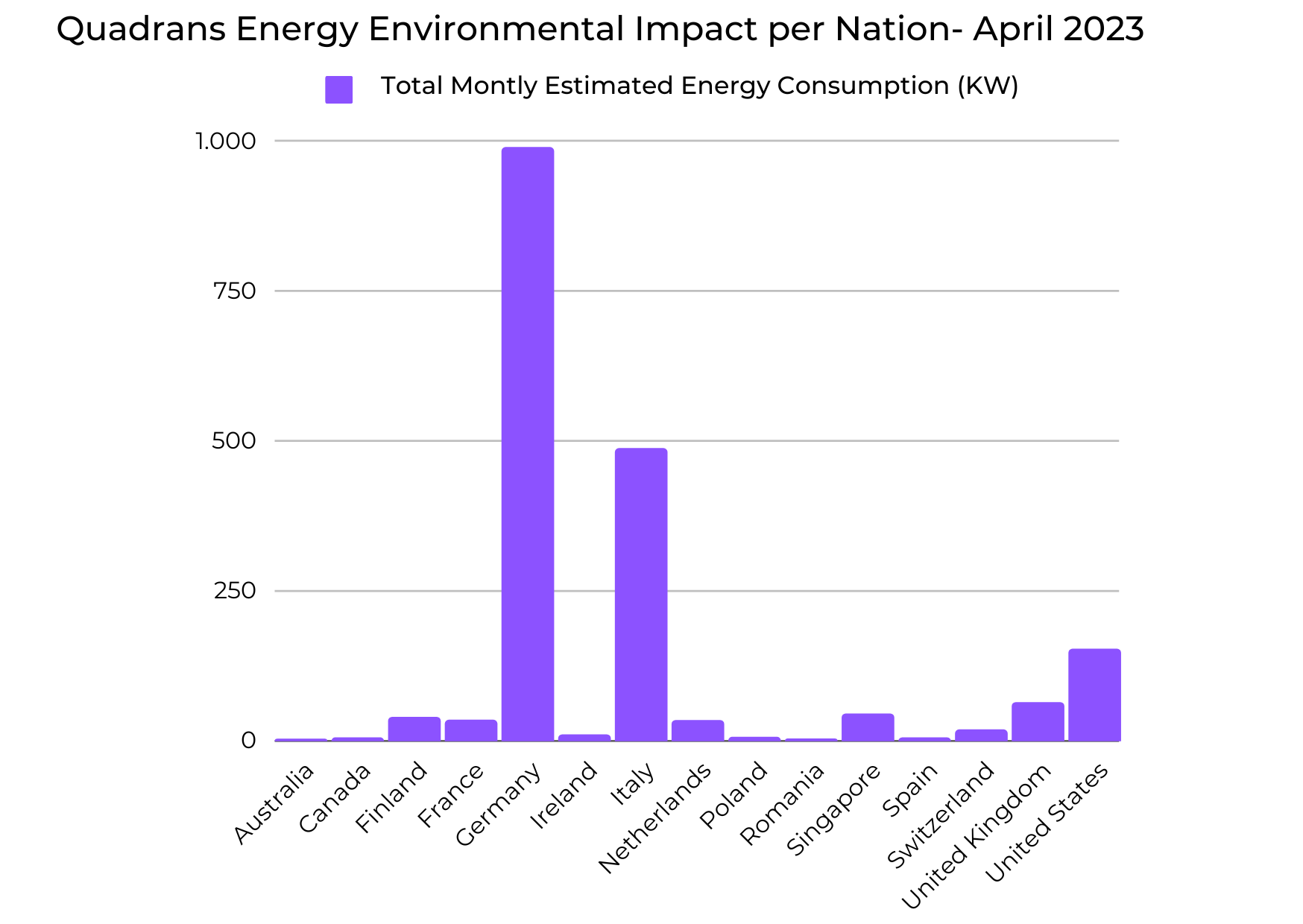
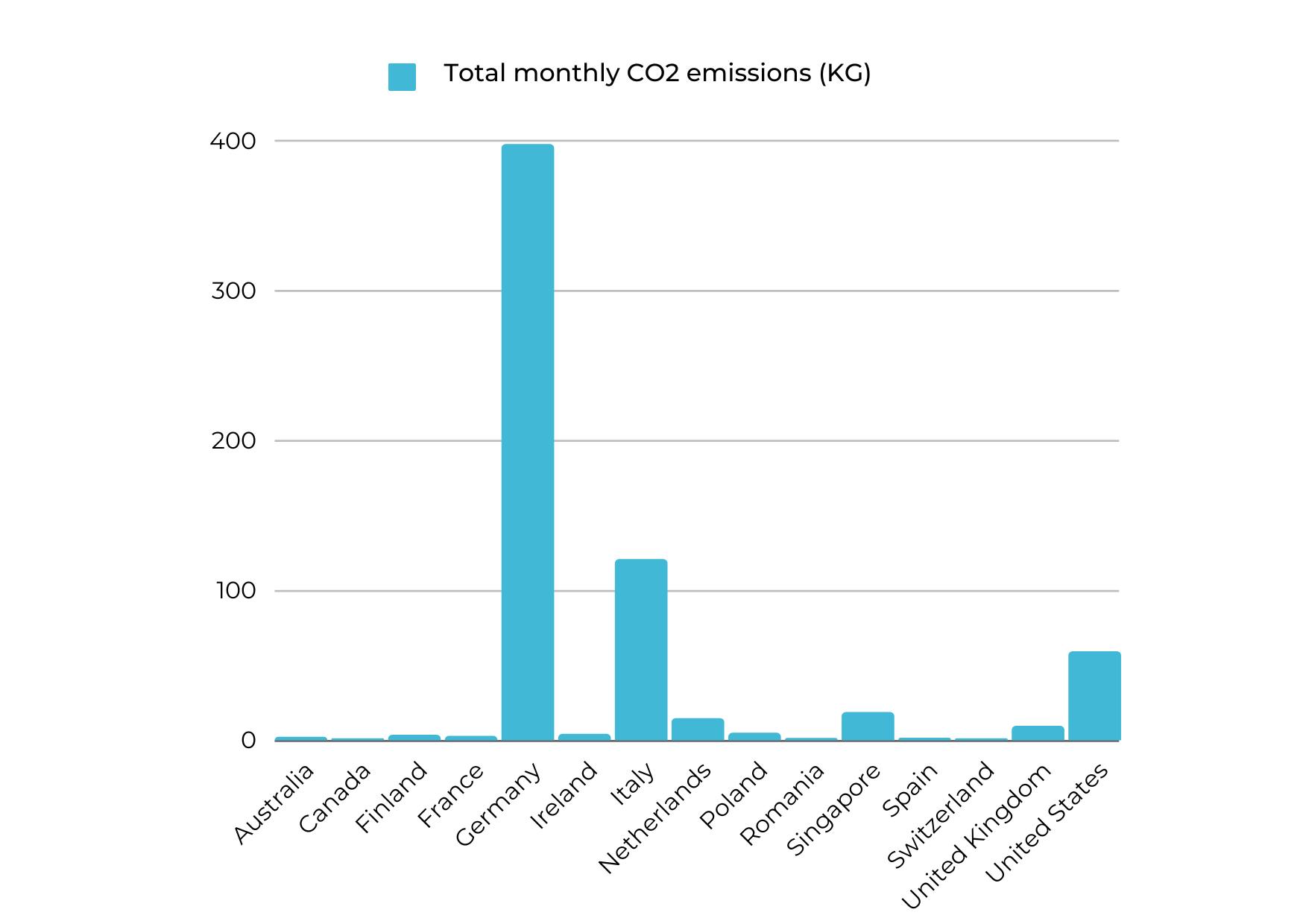
The Quadrans sustainability report provides a detailed analysis of the carbon footprint of its blockchain network, with a specific focus on its three main entities: Lightnodes, Miners, and Masternodes. The report sheds light on the energy consumption and carbon emissions associated with each entity and provides insights into how Quadrans is working towards reducing its overall environmental impact.
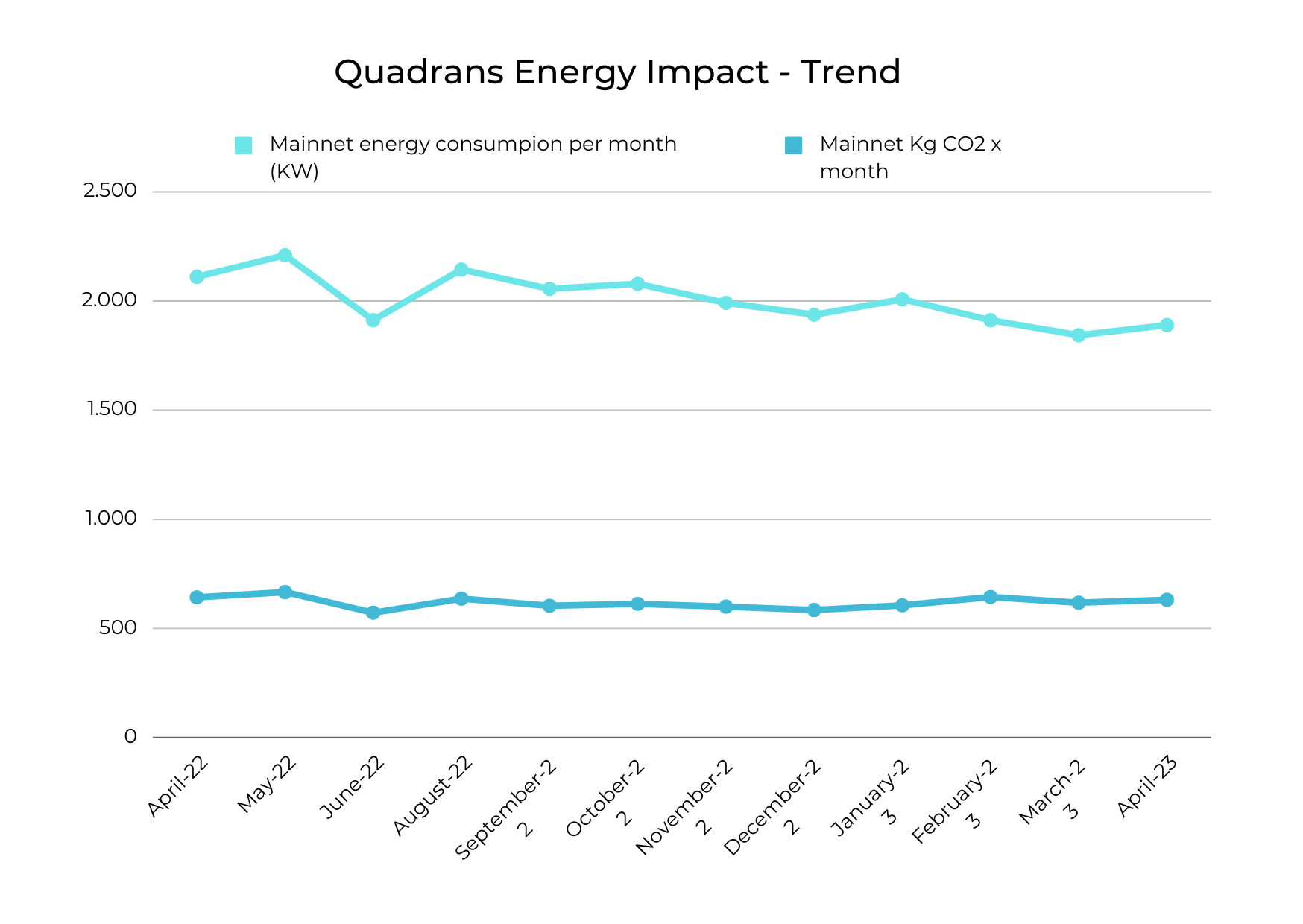
The sustainability report also indicates that the validator network has remained stable over time, with a slight decrease in activity compared to the previous month. This stability supports the network's overall strength and decentralization goals. Additionally, any resulting emissions will be mitigated through continued network development. The report highlights an increase of 2.52% in the overall network consumption (Kw/h) for this month and the CO2 emitted raised by 2,12%.
| Mainnet energy consumption per month (KW) | Mainnet Kg CO2 per month | Energy per transaction considering 60K TPS (W) | gCO2 x Transaction (Considering 60K TPS) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Current Month | 1890,00112 | 634,633 | 0,00001216 | 0,000004081 |
| Delta on previous month | 2,52% | 2,12% | 2,52% | 2,12% |
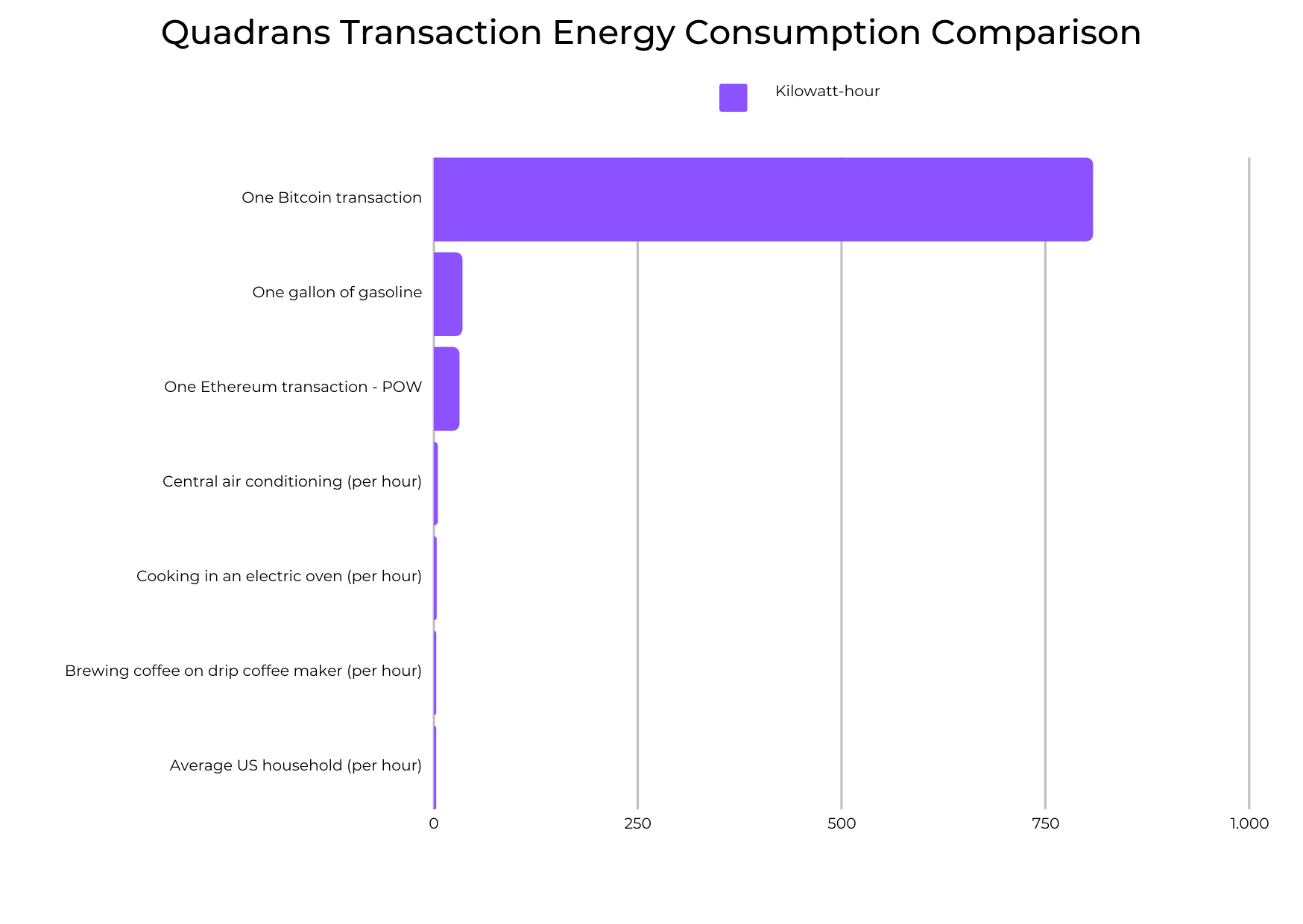
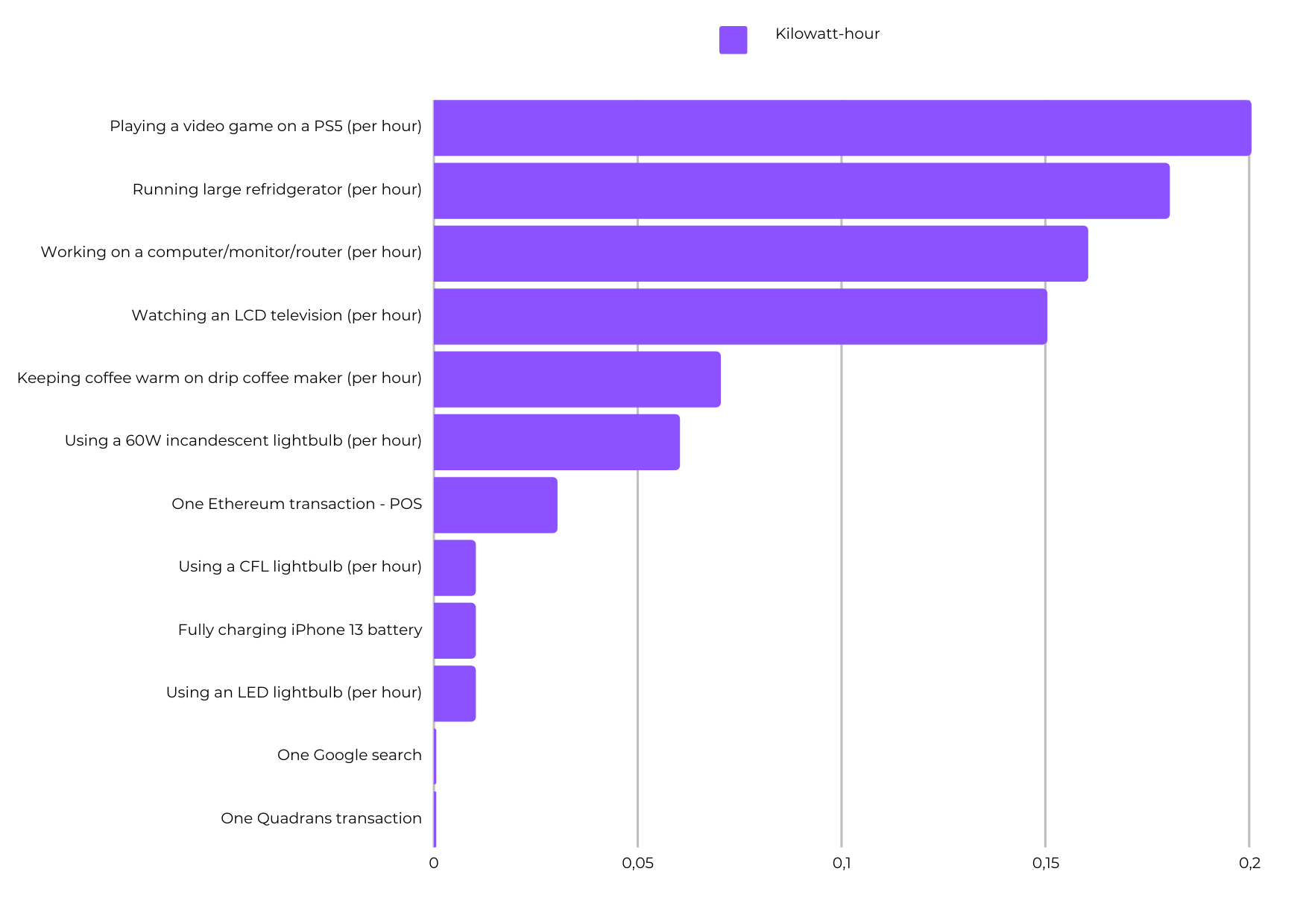
An average Quadrans transaction uses only 0.000012 watts, which is remarkably low and 20 times less energy intensive than a Google search.
Although the average energy use of Quadrans transactions is increasing due to the network's expansion and adoption, it is still significantly lower than the energy consumption of any Proof-of-Work blockchain like Ethereum (which is equivalent to 2.43 billion Quadrans transactions) and Bitcoin (which is equivalent to 65.45 billion Quadrans transactions).
Compared to Ethereum post-merge, which requires the same amount of energy as 2.4 million Quadrans transactions, Quadrans still maintains a significantly lower energy consumption.
Please find more comparisons in the "Comparison" section.
In evaluating grants for new projects, the Quadrans Foundation prioritizes the distribution of its energy impact and considers the carbon footprint of its nodes. The Foundation is committed not only to promoting the overall distribution of the consensus but also to mitigating energy consumption in specific areas, no matter how low it may be.
The Foundation provides comprehensive sustainability reports that analyse the network activity and carbon footprint, setting a positive example for other blockchain networks to follow. Overall, Quadrans demonstrates its commitment to sustainable development by researching and implementing energy-efficient technologies to ensure the network remains environmentally friendly as it grows.
To put the energy efficiency of Quadrans into perspective, consider this: the energy intensity of a single Quadrans transaction is comparable to walking to the nearest supermarket, while the energy required for a single Bitcoin transaction is equivalent to traveling the maximum distance between Earth and the Sun (about 150 billion km).
To make it more tangible, it takes less energy to fully charge an iPhone 13 battery than to perform 1 million Quadrans transactions.
The Quadrans blockchain sustainability report features a trend chart that displays data on the energy consumption and CO2 emissions of the Mainnet Network from April 2022 to April 2023. The chart shows a general upward trend in energy consumption and CO2 emissions, with the highest values being recorded in May, August, and October 2022. However, the trend also shows some fluctuations, including a decrease in energy and CO2 footprint from September 2022 to April 2023. The report provides insight into the network's energy usage over time and highlights the importance of continued efforts to improve energy efficiency and reduce environmental impact.
In conclusion, the Quadrans blockchain sets an example in sustainability and energy efficiency, consuming significantly less energy compared to other blockchain networks. The Quadrans Foundation's commitment to mitigating energy consumption and distributing its energy impact demonstrates its dedication to sustainability. The detailed sustainability report, including trend charts and comparative analysis, provides valuable insights that could serve as a model for other blockchain networks seeking to reduce their carbon footprint.